# MyBatis 源码分析(六):statement 解析
Mapper 映射文件解析的最后一步是解析所有 statement 元素,即 select、insert、update、delete 元素,这些元素中可能会包含动态 SQL,即使用 ${} 占位符或 if、choose、where 等元素动态组成的 SQL。动态 SQL 功能正是 MyBatis 强大的所在,其解析过程也是十分复杂的。
# 解析工具
为了方便 statement 的解析,MyBatis 提供了一些解析工具。
# Token 解析
MyBatis 支持使用 ${} 或 #{} 类型的 token 作为动态参数,不仅文本中可以使用 token,xml 元素中的属性等也可以使用。
# GenericTokenParser
GenericTokenParser 是 MyBatis 提供的通用 token 解析器,其解析逻辑是根据指定的 token 前缀和后缀搜索 token,并使用传入的 TokenHandler 对文本进行处理。
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token 搜索 token 前缀
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
// 没有 token 前缀,返回原文本
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
// 当前解析偏移量
int offset = 0;
// 已解析文本
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// 当前占位符内的表达式
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// 如果待解析属性前缀被转义,则去掉转义字符,加入已解析文本
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
// 更新解析偏移量
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
// 前缀前面的部分加入已解析文本
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
// 更新解析偏移量
offset = start + openToken.length();
// 获取对应的后缀索引
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// 后缀被转义,加入已解析文本
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
// 寻找下一个后缀
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
// 找到后缀,获取占位符内的表达式
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// 找不到后缀,前缀之后的部分全部加入已解析文本
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// 能够找到后缀,追加 token 处理器处理后的文本
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
// 更新解析偏移量
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
// 寻找下一个前缀,重复解析表达式
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
// 将最后的部分加入已解析文本
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
// 返回解析后的文本
return builder.toString();
}
由于 GenericTokenParser 的 token 前后缀和具体解析逻辑都是可指定的,因此基于 GenericTokenParser 可以实现对不同 token 的定制化解析。
# TokenHandler
TokenHandler 是 token 处理器抽象接口。实现此接口可以定义 token 以何种方式被解析。
public interface TokenHandler {
/**
* 对 token 进行解析
*
* @param content 待解析 token
* @return
*/
String handleToken(String content);
}
# PropertyParser
PropertyParser 是 token 解析的一种具体实现,其指定对 ${} 类型 token 进行解析,具体解析逻辑由其内部类 VariableTokenHandler 实现:
/**
* 对 ${} 类型 token 进行解析
*
* @param string
* @param variables
* @return
*/
public static String parse(String string, Properties variables) {
VariableTokenHandler handler = new VariableTokenHandler(variables);
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
return parser.parse(string);
}
/**
* 根据配置属性对 ${} token 进行解析
*/
private static class VariableTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
/**
* 预先设置的属性
*/
private final Properties variables;
/**
* 是否运行使用默认值,默认为 false
*/
private final boolean enableDefaultValue;
/**
* 默认值分隔符号,即如待解析属性 ${key:default},key 的默认值为 default
*/
private final String defaultValueSeparator;
private VariableTokenHandler(Properties variables) {
this.variables = variables;
this.enableDefaultValue = Boolean.parseBoolean(getPropertyValue(KEY_ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE, ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE));
this.defaultValueSeparator = getPropertyValue(KEY_DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR, DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR);
}
private String getPropertyValue(String key, String defaultValue) {
return (variables == null) ? defaultValue : variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
if (variables != null) {
String key = content;
if (enableDefaultValue) {
// 如待解析属性 ${key:default},key 的默认值为 default
final int separatorIndex = content.indexOf(defaultValueSeparator);
String defaultValue = null;
if (separatorIndex >= 0) {
key = content.substring(0, separatorIndex);
defaultValue = content.substring(separatorIndex + defaultValueSeparator.length());
}
if (defaultValue != null) {
// 使用默认值
return variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
}
if (variables.containsKey(key)) {
// 不使用默认值
return variables.getProperty(key);
}
}
// 返回原文本
return "${" + content + "}";
}
}
VariableTokenHandler 实现了 TokenHandler 接口,其构造方法允许传入一组 Properties 用于获取 token 表达式的值。如果开启了使用默认值,则表达式 ${key:default} 会在 key 没有映射值的时候使用 default 作为默认值。
# 特殊容器
# StrictMap
Configuration 中的 StrictMap 继承了 HashMap,相对于 HashMap,其存取键值的要求更为严格。put 方法不允许添加相同的 key,并获取最后一个 . 后的部分作为 shortKey,如果 shortKey 也重复了,其会向容器中添加一个 Ambiguity 对象,当使用 get 方法获取这个 shortKey 对应的值时,就会抛出异常。get 方法对于不存在的 key 也会抛出异常。
public V put(String key, V value) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
// 重复 key 异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key
+ (conflictMessageProducer == null ? "" : conflictMessageProducer.apply(super.get(key), value)));
}
if (key.contains(".")) {
// 获取最后一个 . 后的部分作为 shortKey
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
// shortKey 不允许重复,否则在获取时异常
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
return super.put(key, value);
}
public V get(Object key) {
V value = super.get(key);
if (value == null) {
// key 不存在抛异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " does not contain value for " + key);
}
// 重复的 key 抛异常
if (value instanceof Ambiguity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(((Ambiguity) value).getSubject() + " is ambiguous in " + name
+ " (try using the full name including the namespace, or rename one of the entries)");
}
return value;
}
# ContextMap
ContextMap 是 DynamicContext 的静态内部类,用于保存 sql 上下文中的绑定参数。
static class ContextMap extends HashMap<String, Object> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2977601501966151582L;
/**
* 参数对象
*/
private MetaObject parameterMetaObject;
public ContextMap(MetaObject parameterMetaObject) {
this.parameterMetaObject = parameterMetaObject;
}
@Override
public Object get(Object key) {
// 先根据 key 查找原始容器
String strKey = (String) key;
if (super.containsKey(strKey)) {
return super.get(strKey);
}
// 再进入参数对象查找
if (parameterMetaObject != null) {
// issue #61 do not modify the context when reading
return parameterMetaObject.getValue(strKey);
}
return null;
}
}
# OGNL 工具
# OgnlCache
OGNL 工具支持通过字符串表达式调用 Java 方法,但是其实现需要对 OGNL 表达式进行编译,为了提高性能,MyBatis 提供 OgnlCache 工具类用于对 OGNL 表达式编译结果进行缓存。
/**
* 根据 ognl 表达式和参数计算值
*
* @param expression
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static Object getValue(String expression, Object root) {
try {
Map context = Ognl.createDefaultContext(root, MEMBER_ACCESS, CLASS_RESOLVER, null);
return Ognl.getValue(parseExpression(expression), context, root);
} catch (OgnlException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error evaluating expression '" + expression + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
/**
* 编译 ognl 表达式并放入缓存
*
* @param expression
* @return
* @throws OgnlException
*/
private static Object parseExpression(String expression) throws OgnlException {
Object node = expressionCache.get(expression);
if (node == null) {
// 编译 ognl 表达式
node = Ognl.parseExpression(expression);
// 放入缓存
expressionCache.put(expression, node);
}
return node;
}
# ExpressionEvaluator
ExpressionEvaluator 是 OGNL 表达式计算工具,evaluateBoolean 和 evaluateIterable 方法分别根据传入的表达式和参数计算出一个 boolean 值或一个可迭代对象。
/**
* 计算 ognl 表达式 true / false
*
* @param expression
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
public boolean evaluateBoolean(String expression, Object parameterObject) {
// 根据 ognl 表达式和参数计算值
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, parameterObject);
// true / false
if (value instanceof Boolean) {
return (Boolean) value;
}
// 不为 0
if (value instanceof Number) {
return new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(value)).compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) != 0;
}
// 不为 null
return value != null;
}
/**
* 计算获得一个可迭代的对象
*
* @param expression
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
public Iterable<?> evaluateIterable(String expression, Object parameterObject) {
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, parameterObject);
if (value == null) {
throw new BuilderException("The expression '" + expression + "' evaluated to a null value.");
}
if (value instanceof Iterable) {
// 已实现 Iterable 接口
return (Iterable<?>) value;
}
if (value.getClass().isArray()) {
// 数组转集合
// the array may be primitive, so Arrays.asList() may throw
// a ClassCastException (issue 209). Do the work manually
// Curse primitives! :) (JGB)
int size = Array.getLength(value);
List<Object> answer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Object o = Array.get(value, i);
answer.add(o);
}
return answer;
}
if (value instanceof Map) {
// Map 获取 entry
return ((Map) value).entrySet();
}
throw new BuilderException("Error evaluating expression '" + expression + "'. Return value (" + value + ") was not iterable.");
}
# 解析逻辑
MyBastis 中调用 XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode 方法解析单个 statement 元素。此方法中除了逐个获取元素属性,还对 include 元素、selectKey 元素进行解析,创建了 sql 生成对象 SqlSource,并将 statement 的全部信息聚合到 MappedStatement 对象中。
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 获取 id
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// 自定义数据库厂商信息
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 不符合当前数据源对应的数据厂商信息的语句不加载
return;
}
// 获取元素名
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 元素名转为对应的 SqlCommandType 枚举
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 是否为查询
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 获取 flushCache 属性,查询默认为 false,其它默认为 true
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// 获取 useCache 属性,查询默认为 true,其它默认为 false
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
// 获取 resultOrdered 属性,默认为 false
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
// 解析 include 属性
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 参数类型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
// 获取 Mapper 语法类型
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
// 默认使用 XMLLanguageDriver
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
// 解析 selectKey 元素
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 获取 KeyGenerator
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
// 获取解析完成的 KeyGenerator 对象
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
// 如果开启了 useGeneratedKeys 属性,并且为插入类型的 sql 语句、配置了 keyProperty 属性,则可以批量自动设置属性
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 生成有效 sql 语句和参数绑定对象
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// sql 类型
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 分批获取数据的数量
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
// 执行超时时间
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
// 参数映射
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
// 返回值类型
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
// 返回值映射 map
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
// 结果集类型
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
// 插入、更新生成键值的字段
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
// 插入、更新生成键值的列
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
// 指定多结果集名称
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 新增 MappedStatement
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
# 语法驱动
LanguageDriver 是 statement 创建语法驱动,默认实现为 XMLLanguageDriver,其提供 createSqlSource 方法用于使用 XMLScriptBuilder 创建 sql 生成对象。
# 递归解析 include
include 元素是 statement 元素的子元素,通过 refid 属性可以指向在别处定义的 sql fragments。
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
// 拷贝全局配置中设置的额外配置属性
Optional.ofNullable(configurationVariables).ifPresent(variablesContext::putAll);
applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false);
}
/**
* 递归解析 statement 元素中的 include 元素
*
* Recursively apply includes through all SQL fragments.
* @param source Include node in DOM tree
* @param variablesContext Current context for static variables with values
*/
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) {
// include 元素,从全局配置中找对应的 sql 节点并 clone
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
// 读取 include 子元素中的 property 元素,获取全部属性
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in attribute values
// include 指向的 sql clone 节点,逐个对属性进行解析
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
// statement 元素中可能包含 include 子元素
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
} else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE
&& !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in text node
// 替换元素值,如果使用了 ${} 占位符,会对 token 进行解析
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
/**
* 从全局配置中找对应的 sql fragment
*
* @param refid
* @param variables
* @return
*/
private Node findSqlFragment(String refid, Properties variables) {
// 解析 refid
refid = PropertyParser.parse(refid, variables);
// namespace.refid
refid = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(refid, true);
try {
// 从全局配置中找对应的 sql fragment
XNode nodeToInclude = configuration.getSqlFragments().get(refid);
return nodeToInclude.getNode().cloneNode(true);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// sql fragments 定义在全局配置中的 StrictMap 中,获取不到会抛出异常
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find SQL statement to include with refid '" + refid + "'", e);
}
}
private String getStringAttribute(Node node, String name) {
return node.getAttributes().getNamedItem(name).getNodeValue();
}
/**
* Read placeholders and their values from include node definition.
*
* 读取 include 子元素中的 property 元素
* @param node Include node instance
* @param inheritedVariablesContext Current context used for replace variables in new variables values
* @return variables context from include instance (no inherited values)
*/
private Properties getVariablesContext(Node node, Properties inheritedVariablesContext) {
Map<String, String> declaredProperties = null;
// 解析 include 元素中的 property 子元素
NodeList children = node.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
Node n = children.item(i);
if (n.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
// include 运行包含 property 元素
String name = getStringAttribute(n, "name");
// Replace variables inside
String value = PropertyParser.parse(getStringAttribute(n, "value"), inheritedVariablesContext);
if (declaredProperties == null) {
declaredProperties = new HashMap<>();
}
if (declaredProperties.put(name, value) != null) {
// 不允许添加同名属性
throw new BuilderException("Variable " + name + " defined twice in the same include definition");
}
}
}
if (declaredProperties == null) {
return inheritedVariablesContext;
} else {
// 聚合属性配置
Properties newProperties = new Properties();
newProperties.putAll(inheritedVariablesContext);
newProperties.putAll(declaredProperties);
return newProperties;
}
}
在开始解析前,从全局配置中获取全部的属性配置,如果 include 元素中有 property 元素,解析并获取键值,放入 variablesContext 中,在后续处理中针对可能出现的 ${} 类型 token 使用 PropertyParser 进行解析。
因为解析 statement 元素前已经加载过 sql 元素,因此会根据 include 元素的 refid 属性查找对应的 sql fragments,如果全局配置中无法找到就会抛出异常;如果能够找到则克隆 sql 元素并插入到当前 xml 文档中。
# 解析 selectKey
selectKey 用于指定 sql 在 insert 或 update 语句执行前或执行后生成或获取列值,在 MyBatis 中 selectKey 也被当做 statement 语句进行解析并设置到全局配置中。单个 selectKey 元素会以SelectKeyGenerator 对象的形式进行保存用于后续调用。
private void parseSelectKeyNode(String id, XNode nodeToHandle, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver langDriver, String databaseId) {
// 返回值类型
String resultType = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 对应字段名
String keyProperty = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
// 对应列名
String keyColumn = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
// 是否在父sql执行前执行
boolean executeBefore = "BEFORE".equals(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("order", "AFTER"));
//defaults
boolean useCache = false;
boolean resultOrdered = false;
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
boolean flushCache = false;
String parameterMap = null;
String resultMap = null;
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = null;
// 创建 sql 生成对象
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass);
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 将 KeyGenerator 生成 sql 作为 MappedStatement 加入全局对象
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, null);
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
MappedStatement keyStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(id, false);
// 包装为 SelectKeyGenerator 对象
configuration.addKeyGenerator(id, new SelectKeyGenerator(keyStatement, executeBefore));
}
在 selectKey 解析完成后,按指定的 namespace 规则从全局配置中获取 SelectKeyGenerator 对象,等待创建 MappedStatement 对象。如果未指定 selectKey 元素,但是全局配置中开启了 useGeneratedKeys,并且指定 insert 元素的 useGeneratedKeys 属性为 true,则 MyBatis 会指定 Jdbc3KeyGenerator 作为 useGeneratedKeys 的默认实现。
# 创建 sql 生成对象
# SqlSource
SqlSource 是 sql 生成抽象接口,其提供 getBoundSql 方法用于根据参数生成有效 sql 语句和参数绑定对象 BoundSql。在生成 statement 元素的解析结果 MappedStatement 对象前,需要先创建 sql 生成对象,即 SqlSource 对象。
public interface SqlSource {
/**
* 根据参数生成有效 sql 语句和参数绑定对象
*
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
# SqlNode
SqlNode 是 sql 节点抽象接口。sql 节点指的是 statement 中的组成部分,如果简单文本、if 元素、where 元素等。SqlNode 提供 apply 方法用于判断当前 sql 节点是否可以加入到生效的 sql 语句中。
public interface SqlNode {
/**
* 根据条件判断当前 sql 节点是否可以加入到生效的 sql 语句中
*
* @param context
* @return
*/
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
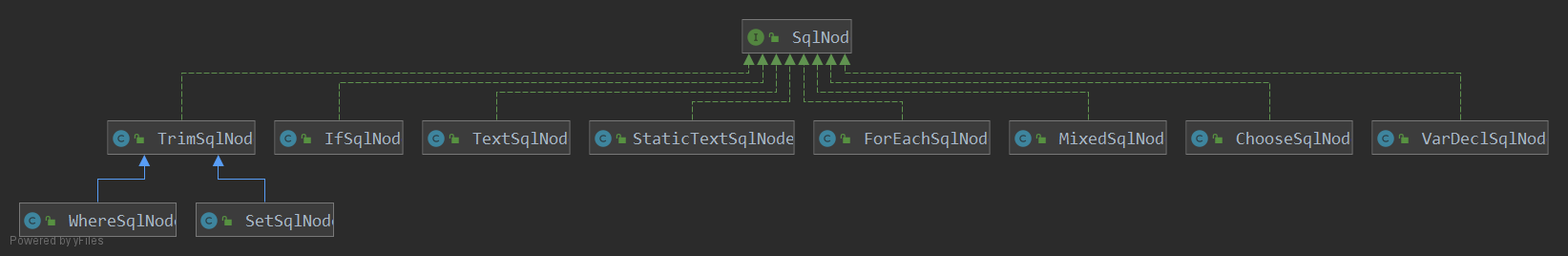
# DynamicContext
DynamicContext 是动态 sql 上下文,用于保存绑定参数和生效 sql 节点。DynamicContext 使用 ContextMap 作为参数绑定容器。由于动态 sql 是根据参数条件组合生成 sql,DynamicContext 还提供了对 sqlBuilder 修改和访问方法,用于添加有效 sql 节点和生成 sql 文本。
/**
* 生效的 sql 部分,以空格相连
*/
private final StringJoiner sqlBuilder = new StringJoiner(" ");
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuilder.add(sql);
}
public String getSql() {
return sqlBuilder.toString().trim();
}
# 节点解析
将 statement 元素转为 sql 生成对象依赖于 LanguageDriver 的 createSqlSource 方法,此方法中创建 XMLScriptBuilder 对象,并调用 parseScriptNode 方法对 sql 组成节点逐个解析并进行组合。
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 递归解析各 sql 节点
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (isDynamic) {
// 动态 sql
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
// 原始文本 sql
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
/**
* 处理 statement 各 SQL 组成部分,并进行组合
*/
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
// SQL 各组成部分
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历子元素
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// 解析 sql 文本
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
// 判断是否为动态 sql,包含 ${} 占位符即为动态 sql
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// 静态 sql 元素
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
// 如果是子元素
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 获取支持的子元素语法处理器
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
// 根据子元素标签类型使用对应的处理器处理子元素
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
// 包含标签元素,认定为动态 SQL
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
parseDynamicTags 方法会对 sql 各组成部分进行分解,如果 statement 元素包含 ${} 类型 token 或含有标签子元素,则认为当前 statement 是动态 sql,随后 isDynamic 属性会被设置为 true。对于文本节点,如 sql 纯文本和仅含 ${} 类型 token 的文本,会被包装为 StaticTextSqlNode 或 TextSqlNode 加入到 sql 节点容器中,而其它元素类型的 sql 节点会经过 NodeHandler 的 handleNode 方法处理过之后才能加入到节点容器中。nodeHandlerMap 定义了不同动态 sql 元素节点与 NodeHandler 的关系:
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}
# MixedSqlNode
MixedSqlNode 中定义了一个 SqlNode 集合,用于保存 statement 中包含的全部 sql 节点。其生成有效 sql 的逻辑为逐个判断节点是否有效。
/**
* 组合 SQL 各组成部分
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
/**
* SQL 各组装成部分
*/
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 逐个判断各个 sql 节点是否能生效
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}
# StaticTextSqlNode
StaticTextSqlNode 中仅包含静态 sql 文本,在组装时会直接追加到 sql 上下文的有效 sql 中:
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
# TextSqlNode
TextSqlNode 中的 sql 文本包含 ${} 类型 token,使用 GenericTokenParser 搜索到 token 后会使用 BindingTokenParser 对 token 进行解析,解析后的文本会被追加到生效 sql 中。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 搜索 ${} 类型 token 节点
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
// 解析 token 并追加解析后的文本到生效 sql 中
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
private static class BindingTokenParser implements TokenHandler {
private DynamicContext context;
private Pattern injectionFilter;
public BindingTokenParser(DynamicContext context, Pattern injectionFilter) {
this.context = context;
this.injectionFilter = injectionFilter;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 获取绑定参数
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
// 计算 ognl 表达式的值
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null"
checkInjection(srtValue);
return srtValue;
}
}
# IfSqlNode
if 标签用于在 test 条件生效时才追加标签内的文本。
...
<if test="userId > 0">
AND user_id = #{userId}
</if>
IfSqlNode 保存了 if 元素下的节点内容和 test 表达式,在生成有效 sql 时会根据 OGNL 工具计算 test 表达式是否生效。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 根据 test 表达式判断当前节点是否生效
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
# TrimSqlNode
trim 标签用于解决动态 sql 中由于条件不同不能拼接正确语法的问题。
SELECT * FROM test
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR">
<if test="a > 0">
a = #{a}
</if>
<if test="b > 0">
OR b = #{b}
</if>
<if test="c > 0">
AND c = #{c}
</if>
</trim>
如果没有 trim 标签,这个 statement 的有效 sql 最终可能会是这样的:
SELECT * FROM test OR b = #{b}
但是加上 trim 标签,生成的 sql 语法是正确的:
SELECT * FROM test WHERE b = #{b}
prefix 属性用于指定 trim 节点生成的 sql 语句的前缀,prefixOverrides 则会指定生成的 sql 语句的前缀需要去除的部分,多个需要去除的前缀可以使用 | 隔开。suffix 与 suffixOverrides 的功能类似,但是作用于后缀。
TrimSqlNode 首先调用 parseOverrides 对 prefixOverrides 和 suffixOverrides 进行解析,通过 | 分隔,分别加入字符串集合。
private static List<String> parseOverrides(String overrides) {
if (overrides != null) {
// 解析 token,按 | 分隔
final StringTokenizer parser = new StringTokenizer(overrides, "|", false);
final List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(parser.countTokens());
while (parser.hasMoreTokens()) {
// 保存为字符串集合
list.add(parser.nextToken().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
}
return list;
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
在调用包含的 SqlNode 的 apply 方法后还会调用 FilteredDynamicContext 的 applyAll 方法处理前缀和后缀。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
FilteredDynamicContext filteredDynamicContext = new FilteredDynamicContext(context);
boolean result = contents.apply(filteredDynamicContext);
// 加上前缀和和后缀,并去除多余字段
filteredDynamicContext.applyAll();
return result;
}
对于已经生成的 sql 文本,分别根据规则加上和去除指定前缀和后缀。
public void applyAll() {
sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder(sqlBuffer.toString().trim());
String trimmedUppercaseSql = sqlBuffer.toString().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.length() > 0) {
// 加上前缀和和后缀,并去除多余字段
applyPrefix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
applySuffix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
}
delegate.appendSql(sqlBuffer.toString());
}
private void applyPrefix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!prefixApplied) {
prefixApplied = true;
if (prefixesToOverride != null) {
// 文本最前去除多余字段
for (String toRemove : prefixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.startsWith(toRemove)) {
sql.delete(0, toRemove.trim().length());
break;
}
}
}
// 在文本最前插入前缀和空格
if (prefix != null) {
sql.insert(0, " ");
sql.insert(0, prefix);
}
}
}
private void applySuffix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!suffixApplied) {
suffixApplied = true;
if (suffixesToOverride != null) {
// 文本最后去除多余字段
for (String toRemove : suffixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove) || trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove.trim())) {
int start = sql.length() - toRemove.trim().length();
int end = sql.length();
sql.delete(start, end);
break;
}
}
}
// 文本最后插入空格和后缀
if (suffix != null) {
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(suffix);
}
}
}
# WhereSqlNode
where 元素与 trim 元素的功能类似,区别在于 where 元素不提供属性配置可以处理的前缀和后缀。
...
<where>
...
</where>
WhereSqlNode 继承了 TrimSqlNode,并指定了需要添加和删除的前缀。
public class WhereSqlNode extends TrimSqlNode {
private static List<String> prefixList = Arrays.asList("AND ","OR ","AND\n", "OR\n", "AND\r", "OR\r", "AND\t", "OR\t");
public WhereSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents) {
// 默认添加 WHERE 前缀,去除 AND、OR 等前缀
super(configuration, contents, "WHERE", prefixList, null, null);
}
}
因此,生成的 sql 语句会自动在最前加上 WHERE,并去除前缀中包含的 AND、OR 等字符串。
# SetSqlNode
set 标签用于 update 语句中。
UPDATE test
<set>
<if test="a > 0">
a = #{a},
</if>
<if test="b > 0">
b = #{b}
</if>
</set>
SetSqlNode 同样继承自 TrimSqlNode,并指定默认添加 SET 前缀,去除 , 前缀和后缀。
public class SetSqlNode extends TrimSqlNode {
private static final List<String> COMMA = Collections.singletonList(",");
public SetSqlNode(Configuration configuration,SqlNode contents) {
// 默认添加 SET 前缀,去除 , 前缀和后缀
super(configuration, contents, "SET", COMMA, null, COMMA);
}
}
# ForEachSqlNode
foreach 元素用于指定对集合循环添加 sql 语句。
...
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
AND itm = #{item} AND idx #{index}
</foreach>
ForEachSqlNode 解析生成有效 sql 的逻辑如下,除了计算 collection 表达式的值、添加前缀、后缀外,还将参数与索引进行了绑定。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 获取绑定参数
Map<String, Object> bindings = context.getBindings();
// 计算 ognl 表达式获取可迭代对象
final Iterable<?> iterable = evaluator.evaluateIterable(collectionExpression, bindings);
if (!iterable.iterator().hasNext()) {
return true;
}
boolean first = true;
// 添加动态语句前缀
applyOpen(context);
// 迭代索引
int i = 0;
for (Object o : iterable) {
DynamicContext oldContext = context;
// 首个元素
if (first || separator == null) {
context = new PrefixedContext(context, "");
} else {
context = new PrefixedContext(context, separator);
}
int uniqueNumber = context.getUniqueNumber();
// Issue #709
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
// entry 集合项索引为 key,集合项为 value
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map.Entry<Object, Object> mapEntry = (Map.Entry<Object, Object>) o;
applyIndex(context, mapEntry.getKey(), uniqueNumber);
applyItem(context, mapEntry.getValue(), uniqueNumber);
} else {
// 绑定集合项索引关系
applyIndex(context, i, uniqueNumber);
// 绑定集合项关系
applyItem(context, o, uniqueNumber);
}
// 对解析的表达式进行替换,如 idx = #{index} AND itm = #{item} 替换为 idx = #{__frch_index_1} AND itm = #{__frch_item_1}
contents.apply(new FilteredDynamicContext(configuration, context, index, item, uniqueNumber));
if (first) {
first = !((PrefixedContext) context).isPrefixApplied();
}
context = oldContext;
i++;
}
// 添加动态语句后缀
applyClose(context);
// 移除原始的表达式
context.getBindings().remove(item);
context.getBindings().remove(index);
return true;
}
/**
* 绑定集合项索引关系
*
* @param context
* @param o
* @param i
*/
private void applyIndex(DynamicContext context, Object o, int i) {
if (index != null) {
context.bind(index, o);
context.bind(itemizeItem(index, i), o);
}
}
/**
* 绑定集合项关系
*
* @param context
* @param o
* @param i
*/
private void applyItem(DynamicContext context, Object o, int i) {
if (item != null) {
context.bind(item, o);
context.bind(itemizeItem(item, i), o);
}
}
对于循环中的 #{} 类型 token,ForEachSqlNode 在内部类 FilteredDynamicContext 中定义了解析规则:
@Override
public void appendSql(String sql) {
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", content -> {
// 对解析的表达式进行替换,如 idx = #{index} AND itm = #{item} 替换为 idx = #{__frch_index_1} AND itm = #{__frch_item_1}
String newContent = content.replaceFirst("^\\s*" + item + "(?![^.,:\\s])", itemizeItem(item, index));
if (itemIndex != null && newContent.equals(content)) {
newContent = content.replaceFirst("^\\s*" + itemIndex + "(?![^.,:\\s])", itemizeItem(itemIndex, index));
}
return "#{" + newContent + "}";
});
delegate.appendSql(parser.parse(sql));
}
类似 idx = #{index} AND itm = #{item} 会被替换为 idx = #{__frch_index_1} AND itm = #{__frch_item_1},而 ForEachSqlNode 也做了参数与索引的绑定,因此在替换时可以快速绑定参数。
# ChooseSqlNode
choose 元素用于生成带默认 sql 文本的语句,当 when 元素中的条件都不生效,就可以使用 otherwise 元素的默认文本。
...
<choose>
<when test="a > 0">
AND a = #{a}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND b = #{b}
</otherwise>
</choose>
ChooseSqlNode 是由 choose 节点和 otherwise 节点组合而成的,在生成有效 sql 于语句时会逐个计算 when 节点的 test 表达式,如果返回 true 则生效当前 when 语句中的 sql。如果均不生效则使用 otherwise 语句对应的默认 sql 文本。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// when 节点根据 test 表达式判断是否生效
for (SqlNode sqlNode : ifSqlNodes) {
if (sqlNode.apply(context)) {
return true;
}
}
// when 节点如果都未生效,且存在 otherwise 节点,则使用 otherwise 节点
if (defaultSqlNode != null) {
defaultSqlNode.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
# VarDeclSqlNode
bind 元素用于绑定一个 OGNL 表达式到一个动态 sql 变量中。
<bind name="pattern" value="'%' + _parameter.getTitle() + '%'" />
VarDeclSqlNode 会计算表达式的值并将参数名和值绑定到参数容器中。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 解析 ognl 表达式
final Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, context.getBindings());
// 绑定参数
context.bind(name, value);
return true;
}
# 创建解析对象与生成可执行 sql
statemen 解析完毕后会创建 MappedStatement 对象,statement 的相关属性以及生成的 sql 创建对象都会被保存到该对象中。MappedStatement 还提供了 getBoundSql 方法用于获取可执行 sql 和参数绑定对象,即 BoundSql 对象。
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 生成可执行 sql 和参数绑定对象
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 获取参数映射
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
// 检查是否有嵌套的 resultMap
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
BoundSql 对象由 DynamicSqlSource 的 getBoundSql 方法生成,在验证各个 sql 节点,生成了有效 sql 后会继续调用 SqlSourceBuilder 将 sql 解析为 StaticSqlSource,即可执行 sql。
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
// 验证各 sql 节点,生成有效 sql
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 将生成的 sql 文本解析为 StaticSqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
此时的 sql 文本中仍包含 #{} 类型 token,需要通过 ParameterMappingTokenHandler 进行解析。
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 创建 #{} 类型 token 搜索对象
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 解析 token
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 创建静态 sql 生成对象,并绑定参数
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
token 的具体解析逻辑为根据表达式的参数名生成对应的参数映射对象,并将表达式转为预编译 sql 的占位符 ?。
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 创建参数映射对象
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
// 将表达式转为预编译 sql 占位符
return "?";
}
最终解析完成的 sql 与参数映射关系集合包装为 StaticSqlSource 对象,该对象在随后的逻辑中通过构造方法创建了 BoundSql 对象。
# 接口解析
除了使用 xml 方式配置 statement,MyBatis 同样支持使用 Java 注解配置。但是相对于 xml 的映射方式,将动态 sql 写在 Java 代码中是不合适的。如果在配置文件中指定了需要注册 Mapper 接口的类或包,MyBatis 会扫描相关类进行注册;在 Mapper 文件解析完成后也会尝试加载 namespace 的同名类,如果存在,则注册为 Mapper 接口。
无论是绑定还是直接注册 Mapper 接口,都是调用 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse 方法来解析的。此方法中的解析方式与上述 xml 解析方式大致相同,区别只在于相关配置参数是从注解中获取而不是从 xml 元素属性中获取。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
// 不允许相同接口重复注册
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
# 小结
statement 解析的最终目的是为每个 statement 创建一个 MappedStatement 对象保存相关定义,在 sql 执行时根据传入参数动态获取可执行 sql 和参数绑定对象。
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder:解析Mapper文件中的select|insert|update|delete元素。org.apache.ibatis.parsing.GenericTokenParser.GenericTokenParser:搜索指定格式token并进行解析。org.apache.ibatis.parsing.TokenHandler:token处理器抽象接口。定义token以何种方式被解析。org.apache.ibatis.parsing.PropertyParser:${}类型token解析器。org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration.StrictMap:封装HashMap,对键值存取有严格要求。org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLIncludeTransformer:include元素解析器。org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource:sql生成抽象接口。根据传入参数生成有效sql语句和参数绑定对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLScriptBuilder:解析statement各个sql节点并进行组合。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.SqlNode:sql节点抽象接口。用于判断当前sql节点是否可以加入到生效的 sql 语句中。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.DynamicContext:动态sql上下文。用于保存绑定参数和生效sql节点。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.OgnlCache:ognl缓存工具,缓存表达式编译结果。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.ExpressionEvaluator:ognl表达式计算工具。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.MixedSqlNode:sql节点组合对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.StaticTextSqlNode:静态sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.TextSqlNode:${}类型sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.IfSqlNode:if元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.TrimSqlNode:trim元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.WhereSqlNode:where元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.SetSqlNode:set元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.ForEachSqlNode:foreach元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.ChooseSqlNode:choose元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.VarDeclSqlNode:bind元素sql节点对象。org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement:statement解析对象。org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql:可执行sql和参数绑定对象。org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.DynamicSqlSource:根据参数动态生成有效sql和绑定参数。org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder:解析#{}类型token并绑定参数对象。